Proteins are the most important building blocks of our body. It is no coincidence that the term ‘protein’ comes from the Greek word ‘proteios’, which means ‘fundamental, primary’. And indeed, proteins play a fundamental role in the human body, as muscles, heart, brain, skin and hair consist mainly of these vital building blocks. The requirement varies depending on the daily physical activity and, for an adult, starts at around 0.83 g per kilogram of body weight. Read on to find out more about proteins, their requirements and proteins in plant-based and animal-based foods, as well as in food supplements.
What are proteins and what are they made of?
Proteins are the building blocks of life and vital for our body. While carbohydrates and fats are primarily used for energy production, proteins are true all-rounders among nutrients: our body uses proteins to build muscles, repair tissue, produce hormones and strengthen the immune system. However, more on this below.
Proteins are made of amino acids. Only 20 different amino acids are needed to form all proteins in the body. Nine of them cannot be produced by our body itself - these are called ‘essential amino acids’. They have to be taken in with food.
Functions and tasks in the body
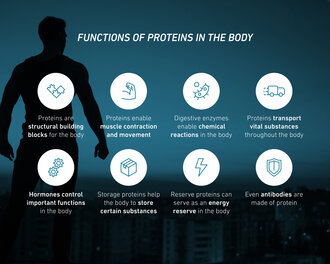
The combination of amino acids determines the specific function of each protein – from muscle growth to wound healing. Proteins can be categorised according to their function, including structural proteins, transport proteins, signalling proteins, storage proteins, motor proteins and enzymes:
- Structural proteins serve as structural building blocks for the body. These include, for example, collagen, which gives skin, bones and tendons their stability, and keratin, which forms hair, nails and the outer layer of skin. These structuralproteins are, so to speak, the ‘scaffolding’ that holds our body together.
- Enzymes are highly specialised proteins that enable and drive chemical reactions in the body – from digestion to metabolism and energy production.
- Transport proteins serve as freighters for vital substances that need to be transported throughout the body. In addition to haemoglobin, which transports oxygen through the blood, and transferrin, which transports iron to the cells, these also include albumin, which distributes fats and hormones in the blood, as well as lipoproteins in LDL and HDL particles that transport cholesterol. Transport proteins also include ion channels – proteins in the cell membranes that regulate the targeted transport of ions such as sodium, potassium or calcium. In this way, they control important bodily functions such as nerve impulses, heartbeat or muscle contraction.
- Hormones are among the signalling proteins. Hormones are messenger substances that reach their target organs via the blood and control important functions such as growth, metabolism and reproduction.
- Storage proteins help the body to store certain substances (e.g. ferritin).
- Reserve proteins: Proteins can also serve as an energy reserve in the body. In times when the intake of fats and carbohydrates is insufficient, amino acids from proteins can be broken down to produce energy.
- Movement proteins: Actin and myosin enable muscle contraction and movement.
- But immunoglobulins (antibodies) and receptors also consist of proteins.
This list shows that proteins fulfil a fascinating range of vital tasks in our body. Without them, human life would not be possible.

What proteins are good for – their benefits:
In our daily diet, proteins are primarily important for building muscle and maintaining it. The branched-chain amino acids, which athletes usually know as BCAAs – an abbreviation derived from the English term ‘branched chain amino acids’ – are particularly important for muscles. These amino acids, which can be obtained from food and dietary supplements, are used in the muscles as an energy supplier or basic building block. For this reason, proteins also play an important role in muscle regeneration.
Proteins are not only important for our sporting performance, they are also important for our hair and skin – as both, as mentioned above, consist largely of proteins themselves. The protein keratin repairs damaged strands and ensures strong and healthy hair. The protein collagen in turn strengthens the skin – and because collagen production decreases with age, it can be useful to take this protein in the form of a dietary supplement.
Structural proteins such as collagen are also extremely important for the health and stability of bones. They give the bones strength and resistance to fractures by forming the ‘scaffolding’, so to speak, that gives them shape and strength. In addition, bone tissue also contains elastin proteins, which ensure that the bones are not brittle and rigid, but elastic and resilient.
Proteins are also essential for bone growth in childhood and adolescence, as they provide the building blocks for the formation of new bone substance.
Even if you break a bone or suffer any other kind of injury, your body needs a lot of proteins to repair the bones and heal the wound. Without the high proportion of proteins in our bodies, our bones would be much more susceptible to fractures and injuries – so proteins play a crucial role in their stability, elasticity and ability to regenerate.
Proteins are also vital for the immune system. They are crucial for building and repairing body tissue and for defending against infections. A deficiency can impair the immune system.
And proteins can even help you lose weight. This is because a higher protein intake is associated with greater satiation and thus greater weight loss in a diet than a lower protein intake. However, you should make sure you get the dosage right – ideally in consultation with a doctor who specialises in nutrition. The right amount of protein not only helps you feel fuller, but also protects our muscle tissue while dieting.
Daily requirement: How much protein do I need?
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recommends that adult humans take in at least 0.83 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight every day. For a person weighing 75 kilograms, that would be 62.25 grams of protein per day.
On average, athletes need a little more: around 1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. For real endurance or strength athletes, the optimal dose is even slightly higher, in the range of 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Recommended daily intake of proteins at a glance:
| Who | Reference value per kg of body weight per day | Daily requirement for an adult weighing 75 kg |
| Children (1-17 years) | 0,83 - 1,14 g | |
| Adults (18-65 years) | 0,83 g | 62 g |
| Elderly (> 65 years) | 1 g | 75 g |
| Pregnancy | 0,83 g | 62 g |
| Pregnancy: 1st Trimester | + 1 g | 63 g |
| Pregnancy: 2nd Trimester | + 9 g | 71 g |
| Pregnancy: 3rd Trimester | + 28 g | 90 g |
| Breastfeeding in the first 6 months | + 19 g | 81 g |
| Breastfeeding after 6 months | + 13 g | 75 g |
| Athletes (> 5h sport / week) | 1,2 - 2,0 g | 90 -150 g |
| Endurance and strenght athletes | 1,6 - 2,2 g | 120 -165 g |
Table 1: Daily protein requirement according to age and special needs
How many protein shakes a day do you need to meet your daily requirement?
There is basically no limit to the number of protein shakes you can have each day. Protein powders can also be used creatively in smoothies or desserts.
Food: Where can you find the most protein?
So now we know that proteins are important for us, whether we do sports or not. But how do you get as much protein as possible from your diet? Tofu is a classic that can be used in many ways because it can be used whole or pureed and takes on any flavour. Other good sources include beans of all kinds, chickpeas and quinoa. If you don't want to go without meat, lean meat is the best source of protein.
In any case, the view that animal proteins contribute better to muscle building or regeneration than plant-based proteins is outdated. The only thing that matters here is the CS (Chemical Score). This refers to a WHO reference protein. The reference protein defines the ratio of amino acids in the protein. A CS of 100 means that the body can almost completely utilise the amino acids from the protein for its own protein. The vegan protein sticks from BIOGENA with a chemical score of 198, are therefore an excellent source of protein.
High protein foods: vegan protein
| Food | Protein per 100 g | Portion size | Protein per portion | DRV (%) per portion |
| Soya protein isolate | 80-90 g | 50 g | 40-45 g | 80-90 % |
| Pea protein powder | 80 g | 50 g | 40 g | 80 % |
| Seitan | 25 g | 100 g | 25 g | 50 % |
| Hemp seeds | 24 g | 30 g | 7,2 g | 14,4 % |
| Lentils (dried) | 23 g | 100 g | 23 g | 46 % |
| Peanuts | 26 g | 30 g | 7,8 g | 15,6 % |
| Pumpkin seeds | 19 g | 30 g | 5,7 g | 11,4 % |
| Chickpease (dried) | 19 g | 100 g | 19 g | 38 % |
| Tempeh | 19 g | 100 g | 19 g | 38 % |
| Almonds | 21 g | 30 g | 6,3 g | 12,6 % |
| Sun flower seeds | 21 g | 30 g | 6,3 g | 12,6 % |
| Black beans (dried) | 21 g | 100 g | 21 g | 42 % |
| Chia seeds | 17 g | 30 g | 5,1 g | 10,2 % |
| Tofu | 8-16 g | 100 g | 8-16 g | 16-32 % |
| Quinoa (raw) | 14 g | 100 g | 14 g | 28 % |
| Amaranth (raw) | 14 g | 100 g | 14 g | 28 % |
| Edamame (boiled) | 11 g | 100 g | 11 g | 22 % |
| Oat flakes | 13 g | 30 g | 3,9 g | 7,8 % |
Table 2: High-protein vegan food
High protein foods: animal protein
| Food | Protein per 100 g | Portion size | Protein per portion | DRV (%) per portion |
| Chicken breast (cooked) | 31 g | 100 g | 31 g | 62 % |
| Tuna (grilled) | 30 g | 100 g | 30 g | 60 % |
| Beef (lean, cooked) | 26 g | 100 g | 26 g | 52 % |
| Salmon (grilled) | 25 g | 100 g | 25 g | 50 % |
| Eggs | 13 g | 1 Egg (50 g) | 6,5 g | 13 % |
| Yoghurt, greek | 10 g | 100 g | 10 g | 20 % |
| Cottage cheese | 11 g | 100 g | 11 g | 22 % |
| Milk (whole milk) | 3,5 g | 1 Glass (200 ml) | 7 g | 14 % |
Table 3: Foods high in animal protein
Good to know: The colloquial term ‘protein’ is not to be confused with the egg white. In fact, the egg white contains less protein than the egg yolk.
High protein recipes
However, mere knowledge of individual foods is not enough to implement a high-protein diet not only on paper but in everyday life. Especially if you are less adept at cooking, high-protein recipes can be a real game-changer. For example, you can prepare protein pancakes with low-fat quark and protein powder, or high-protein feta muffins with Greek sheep's cheese, quark and spinach. A little online research will reveal a wide range of protein-rich dishes, making it easy to incorporate more protein into your diet on a permanent basis.
Are protein shakes useful?
Protein shakes can definitely help you build muscle when combined with intensive strength training. But: the drinks alone are not enough. Regular training is essential for muscle building. People with kidney failure should also be careful not to consume too much protein.
Protein types and their differences
Which is better – vegetable or animal protein? In the context of a balanced diet, there is actually no big difference, provided that the total amount of protein is sufficient. If you tend to eat a rather one-sided diet, a protein shake with a high chemical score (see above for an explanation) can be helpful. It is important to choose foods that are as wholesome as possible – nuts, lentils, beans, lean meat, fish, dairy products or eggs.
Improve protein intake
To optimise protein absorption, it is recommended to spread your protein intake throughout the day. For example, a protein shake at breakfast can help you get off to a protein-rich start to the day. At lunch and dinner, you should then make sure that your protein intake is well distributed so that your body has enough time to digest it and your amino acid levels remain consistently high to supply your muscles with building material.
Protein deficiency in Europe: a rarity, but not unheard of
In Europe, most people have no problem getting enough protein – a real protein deficiency is therefore rare. Nevertheless, there are situations in which people in this country can be affected by a protein deficiency.
Some possible causes are:
- Low intake: People who eat little or an unbalanced diet, such as those on extreme diets or unbalanced vegan diets, often don't get enough protein.
- Increased needs: Older people often need more protein to stay healthy and should therefore pay particular attention to a protein-rich diet.
- Increased loss: Some people lose more protein than they can take in due to their lifestyle or certain physical exertion.
- Plant-based nutrition: For vegans and vegetarians, it is important to choose the right protein sources and to ensure a balanced combination of essential amino acids. By combining different plant-based protein sources, a high biological value can be achieved even without animal products.
Symptoms of a protein deficiency can include muscle weakness, tiredness, slower regeneration and brittle hair and nails. A conscious approach to high-protein foods ensures that the body remains healthy and productive.
Conclusion: proteins are true all-rounders – they promote muscle building, support skin health and provide energy for recovery and performance. In Europe, most people meet their daily protein requirement, but making informed choices about protein-rich foods – and, if needed, supplements such as protein shakes – allows people to get the most out of protein. Protein shakes can be a particularly practical solution for people with increased needs or an active lifestyle, as they provide a quick and flexible way to take in high-quality amino acids. This helps to keep the body strong, healthy and ready for the challenges of everyday life.
Frequently asked questions about protein
Athletes are well served with 1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, serious strength or endurance athletes with about 1.7 grams. Depending on the circumstances, the need can be even higher, for example during the competition season or when on a diet.
Of course, that depends on the size. You get about 12 grams of protein per 100 grams of egg. In other words, a medium egg weighs about 58 grams and provides you with 7 grams of protein.
Increased protein consumption can be very helpful during a diet, as protein protects the existing muscle mass and contributes to the feeling of fullness. In the case of doubt, the exact protein intake should be clarified with a nutritionist. Read more!
Sources and further reading:
Hahn, A. et al. Ernährung. Physiologische Grundlagen, Prävention, Therapie. 2005.
European Food Safety Authority (2012): Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for protein. https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2557
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Ernährung e.V. (2020): Positionspapier zur Proteinzufuhr im Sport. https://www.dge.de/presse/meldungen/2020/positionspapier-zur-proteinzufuhr-im-sport/
AnovonA. Chemical Score – Biologische Wertigkeit. https://anovona.de/chemical-score/
Tanner S., et al. (2018): Recent Perspectives Regarding the Role of Dietary Protein for the Promotion of Muscle Hypertrophy with Resistance Exercise Training. Nutrients. 10(2):180. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29414855/
Jäger, R., et al. (2017): International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 14, 20. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28642676/
Leidy, H.J., et al. (2015): The role of protein in weight loss and maintenance. Am J Clin Nutr, 101(6), 1320S-1329S. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25926512/