Sleep & relaxation
What does good sleep look like and why is it important? People sleep for around one-third of their lives. This alone shows that sleep must be important for your health. In fact: Sufficient and quality night-time recovery is not only necessary for well-being.


Why is a good night's sleep important?
A number of processes take place while we sleep: our memory, learning ability, concentration and immune system are fortified, and regeneration processes run at full capacity. A good night’s sleep can make you feel better, fitter and more efficient. It can even make you look better.
Sleep duration and sleep quality – how much sleep is needed?
The need for nighttime sleep varies greatly between different people. Some people need four to five hours, others eight to nine hours. But at the end of the day, it’s the sleep quality that counts, not the sleep quantity. If you regularly feel fresh and rested when you wake up, you sleep enough. If the alarm clock rips you out of your sleep every day and you haven’t slept enough, your sleep duration is too short or your sleep quality is insufficient. There is no uniform definition of sleep quality. Science assumes that good sleep quality is given if you fall asleep within 30 minutes after going to bed and do not wake up more often than once per night. Once you wake up, you fall asleep again within 20 minutes and the time you spend in bed consists of at least 85% sleep. Some also include the duration of the individual sleep phases in their considerations regarding sleep quality. If you cannot fall asleep, or if you wake up in the morning feeling exhausted, you should think about the quality of your sleep and your sleep habits. If you would like to understand sleep in all its details, you can find help in special sleep laboratories or analyze your sleep and sleep quality from home using sleep trackers that are now fitted to most fitness wearables as standard. There are also special smartphone apps to monitor sleep. Stimuli such as movement, breathing, and heartbeat are measured. As a result, the period of sleep onset as well as the individual sleep phases and their duration can be derived and you learn whether and how often you wake up at night.
Understanding sleep: the 4 phases of sleep
Falling asleep:
This transitional state of five to 20 minutes prepares the body for actual sleep. The body comes to rest. Breathing and pulse become more uniform, and the muscles relax. Brain activity slows down, the brain is at rest. The duration of this phase may vary. People who cannot fall asleep for a longer period often see this as a problem, which in turn causes tension and makes them stay awake for longer.
Stable sleep:
After falling asleep, the phase of stable sleep follows. Now the body functions are further reduced, breathing and heartbeat are slowed, body and mind switch to sleep mode. We normally spend more than half of our sleep in this condition during the night.
Deep sleep:
Regeneration and recovery begin at this stage. The body repairs rejuvenates, and strengthens itself for the new day. In this sleep phase, waking up is the most difficult; you can talk or sleep during this sleep phase. We spend around 20% of our total sleep time in deep sleep.
Dream sleep or REM sleep:
The body is still relaxed, but the brain is active. Characteristic of the REM phase is the rapid back-and-forth movement of the eyes under the closed eyelids (Rapid Eye Movement/REM). Heartbeat and respiratory rate increase and dreaming becomes more intense. Overall, we spend 60 to 75 minutes per night in this phase, which is sometimes similar to the waking state and is therefore also called “paradoxical sleep”.
Tip: Waking up fully rested
During nighttime sleep, we go through the four phases several times, whereby the duration of REM sleep increases during the night. Towards the morning we therefore dream a lot. It is beneficial to wake up when the REM phase is completed and we have gone through a complete sleep cycle. Then when the alarm clock rings, you feel rested and rejuvenated.
The rule of thumb is: 90 minutes per sleep cycle. This allows the most favorable time to fall asleep to be calculated. If you need to get up at 6 a.m., you should ideally fall asleep at 9 p.m., 10:30 p.m. or midnight. A different sleep cycle length can be determined by trying it out. The best time to fall asleep is then quickly determined.
What happens when we sleep?
Sleep, memory, and learning
Sleep is necessary to process what you experience during the day. This separates the important from the unimportant. The brain compares the experiences of the day with memories and experiences. Essential information passes into the memory and is stored thereby strengthening the connections between the nerve cells. The same applies to concentration and mental performance. No wonder that well-rested people perform better in memory tests than those with sleep deficit.
Sleep strengthens the immune system
During sleep, it is not only impressions that are anchored in the long-term memory. The same happens in the immune cells. Recent research results indicate that information about pathogens with which the immune system was in contact during the day is transferred to the memory of the immune cells during deep sleep. Good, adequate sleep therefore helps the body's protection system.
Sleep, regeneration, and a rested appearance
Tissue and cells regenerate as we sleep. Muscles are also built up. The growth hormones responsible for this are released more frequently at night. Whether you have slept enough or not enough is often shown by your skin. It is not for nothing that we speak of beauty sleep.
The brain also regenerates during sleep. Nowadays we know that it is rinsed and cleaned. During sleep, the spaces between the nerve cells increase by about 60 percent and small protein deposits are washed out.

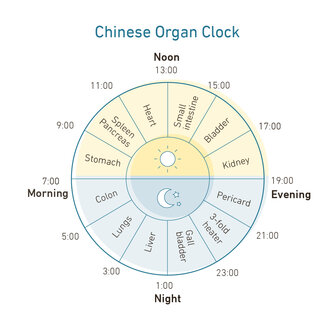
Chinese organ clock: Always awake at the same time?
If you wake up at the same time every night regardless of the time of bedtime, this can be a message from the body according to TCM (Traditional Chinese Medicine). This is because, according to TCM, Qi (life energy) flows through our body via 12 meridians (energy pathways). Each meridian is assigned a specific organ. The organ has a maximum of Qi at a specific time and each meridian for two hours per day. Twelve hours later, it has its energy low. The doctrine states: If the energy flow is disturbed via the meridians, this affects our body and sleep. If you wake up regularly at a certain time, the body is sending important signals.
Frequently asked questions about sleep
People who want to improve their night’s sleep can use different methods. In order to be able to fall asleep relaxed, a calm atmosphere and the right sleep aids should always be ensured and going to bed should be made sleep friendly. You can find out what this looks like in concrete terms in this article.